[8.1] Radians and arclength
Radians
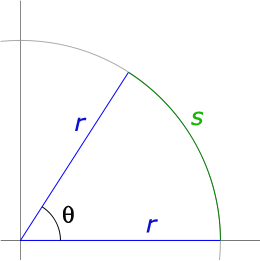
$\theta = s/r$
Therefore, on the unit circle ($r=1$) the length along the arc is the same as the angle in radians.
Converting between degrees and radians
What is the perimeter of a circle? Of a circle with radius $r=1$?
Perimeter = $2\pi r$, Perimeter of a unit circle = $2\pi$.
The measure of a "straight angle" in degrees is $180^o$.
The measure of a "straight angle" in radians would be:
$= \frac{\pi r}{r} = \pi$.
So, considering the straight angles,
$$\pi \text{ radians} = 180^o=\frac 12 \text{ rotations around the circle}.$$
Convert $3\pi/5$ radians to degrees
$\frac{3\pi}{5}{\rm radians } \times \frac{180^o}{\pi\ {\rm rad }} = 108^o$.
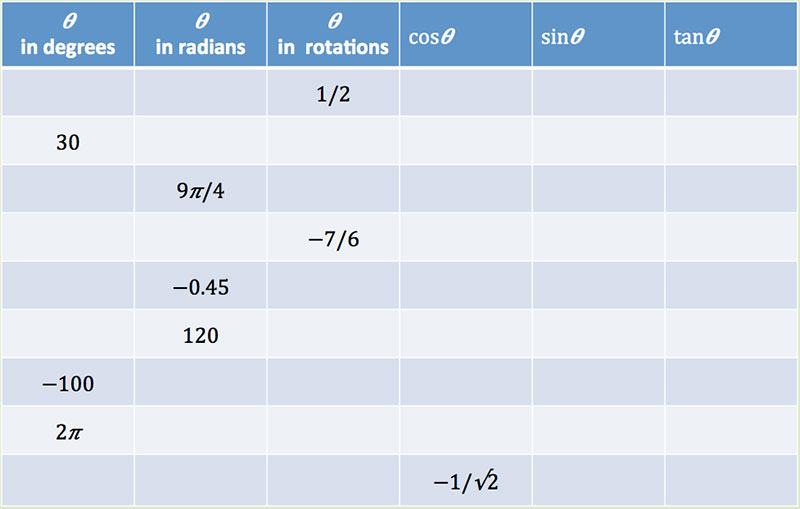
Be able to calculate
Problem 27
What is the length of an arc that is cut off by an angle of $95^o$ in a circle of radius 3 meters?
Problem 48
Using a weight on a string called a plumb bob, it is possible to erect a pole that is exactly vertical, which means that the pole points directly toward the center of the earth. Two such poles are erected one hundred miles apart. If the poles were extended they would meet at the center of the earth at an angle of $1.4333^o$. Compute the radius of the earth from this info.