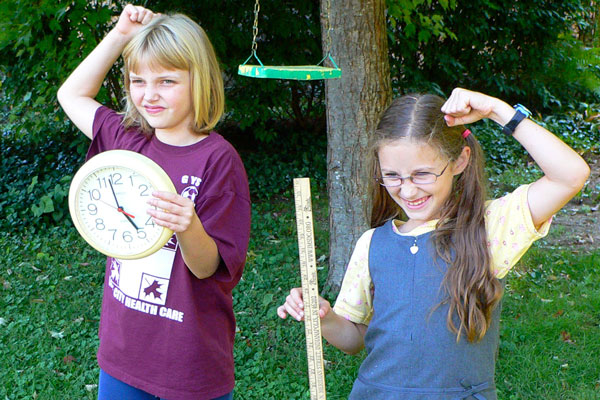

Clocks and meter sticks are all that's needed to characterize motion.

Clocks and meter sticks are all that's needed to characterize motion.
Estimate the distance from GC's 8th street entrance (near dining hall) to the RFC by two methods...
Describing the motion of a moving body...
average speed = distance travelled / time to travel
`s = d / t`
[writing: about speed]
Was their speed always the same at every moment of the trip?
How could you measure your "instantaneous" speed?
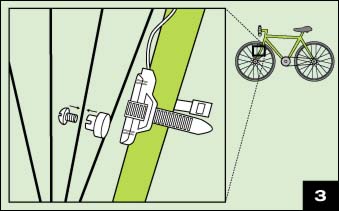 A bicycle speedometer (nowadays called a cyclocomputer) uses a magnet attached to a spoke, and a sensor which "feels" the magnet pass.
A bicycle speedometer (nowadays called a cyclocomputer) uses a magnet attached to a spoke, and a sensor which "feels" the magnet pass.
velocity = speed and direction of travel
Jane passes Fred, both of them moving North on 8th Street.
Jane and Fred pass in opposite directions, both going 15 km / hour.
Jane and Fred are both going North on 8th St at 15 km / hour. But Jane has just crossed College Avenue, and Fred has already passed Plymouth Avenue.
Acceleration: any change in an object's velocity.
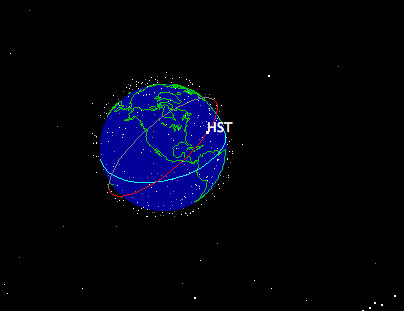
Orbit of the Hubble Space Telescope around the earth.
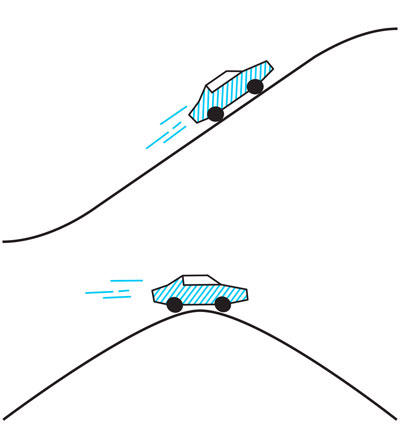 A car...
A car...
These things all mean "Acceleration" in Physics-speak:
What 3 acceleration devices can a car driver control?
We said...
A body that is subject to no external influences* will keep moving, if it was moving to begin with, in a straight line with unchanging speed. Or, if it was at rest, such a body will stay at rest.
But now we can say
A body subject to no external influences must maintain an unchanging velocity.
How do we know objects speed up as they fall?
acceleration = change in speed (m/s) / time interval (s)
On the surface of earth all objects are accelerated by the same amount: 9.8 m/s/s
Conceptual Exercises in Chapter 3: 8, 11, 15, 16, 19, 27.
Problems in Chapter 3: 3, 5